
Numerical solutions are very broad and having access to today's computers, they are more useful than complex analytical solutions 8. Analytical methods are usually used in the hydraulics of wells. In these simplifications, assumptions such as homogeneity and one-dimensional or two-dimensional flow are considered.
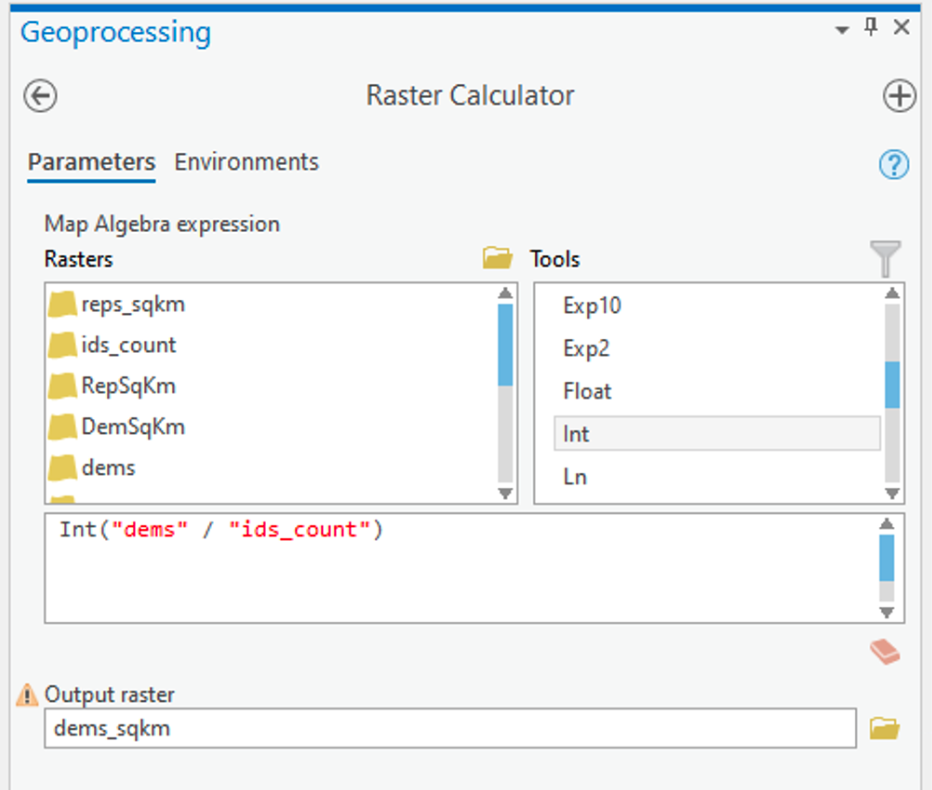
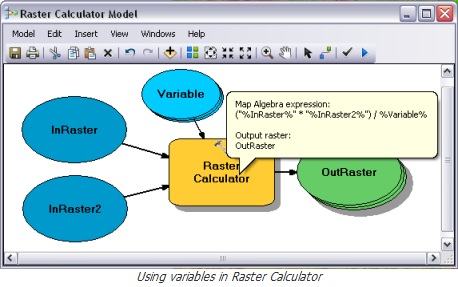
Compare raster calculator and model builder series#
A series of simplifications should be involved in solving the governing equations of the groundwater flow analytically. Numerical methods based on computer use become the main tool in solving problems in the natural environment. The complexity of the aquifer system, the heterogeneity of the geological formations, different amounts of pumping and feeding at different times, etc., make the numerical models a replacement for the analytical models in the natural environment 6, 7. The existing equations in the modeling process of the groundwater table can be solved in the form of a mathematical model in two analytical and numerical ways. This issue complicates the process of managing and simulating these resources. Groundwater resources are not uniformly distributed in all parts of the earth's solid crust.

Also, groundwater can flow naturally to the surface of the earth in the form of springs 5. Groundwater refers to the water that is under the surface of the earth and can be collected in wells, tunnels, and drainage galleries. Therefore, it is important to manage both the development of the agricultural sector and the quality of groundwater resources. However, agriculture is both the cause and the victim of water pollution 3, 4. Water used in agriculture always returns to the surface and groundwater in a chain. On the other hand, agriculture is always considered the biggest consumer of freshwater. Failure to apply appropriate management solutions causes complex and bigger problems such as the spread of diseases caused by polluted water, the death of aquatic animals, and the destruction of wetlands and rivers 1, 2. The development of agriculture due to the increase in population and the demand for food security has led to the pollution of groundwater, which is caused by several factors such as soil erosion, and extreme use of fertilizers and pesticides. Groundwater resources are the most important resources of freshwater available to humans. The DRASTIC vulnerability estimation method is only useful for estimating the areas that have a high potential for contamination and according to the validation tests, it has also provided a suitable estimate.
Due to the agricultural activities with the use of large amounts of fertilizers in this plain, there is a potential for pollution in all of the places, and it requires codified and executive planning for agricultural operations as well as the use of groundwater sources. The highest level of pollution in the aquifer of the plain is related to the southern and southeastern parts of the plain. This shows that the average concentration of this ion in the region is generally high. The results showed that in a wide area of the region, the nitrate ion concentration has values of more than 25 mg/L.

After calibrating the model in permanent conditions, the model was calibrated in non-permanent conditions for 2 years. The results showed that the amount of hydraulic conductivity in the plain for different areas after calibration in steady state was calculated between 0.8 and 34 m/day. For the investigation of temporal changes in groundwater nitrate pollution and the role of agriculture and other sources in the pollution of groundwater, the information on 42 drinking water wells with suitable distribution in the plain in Bouin-Daran Plain in the center of Iran was used. Groundwater assets are the foremost imperative assets of freshwater accessible to people especially in arid and semi-arid regions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
